Finally! OLED comes to laptops at CES 2016 ,AND YOU WON’T BELIEVE YOUR EYES
Laptop displays suck, and have for a long time. Sure, the very best sold today are reasonably good, and their resolution has skyrocketed. But the gamut and contrast of the average laptop panel is disappointing.
Now, for the first time in years, we’re set to see a major revolution in picture quality. This is not just due to Ultra HD, which is rapidly becoming mainstream, but also a display technology that any fanatic of high-end televisions will be familiar with: OLED.
This is not a minor step forward. OLED’s arrival is like an Imperial Star Destroyer showing up for a fight between starfighters. Now that it’s here, everything that’s happened before is insignificant.
Why your laptop display sucks
Perhaps you have a Dell XPS 15, or an Asus Zenbook, and think your screen is quite nice. Relative to other laptops, you’re right. But every laptop display shares a fatal flaw. The backlight.
Every laptop display shares a fatal flaw. The backlight.
The crystals in a normal LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) panel twist to channel light to form an image, but they produce no light of their own. A picture is visible only because lights sit behind the screen and shine through the LCD panel. That works, but it also means it’s impossible to every have a perfectly dark image. The light is always on, to some degree.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is different. Each pixel emits its own light. Individual pixels can turn off entirely, and when they do, they’re pitch black. That vastly improves contrast, and contrast is crucial to rendering a realistic, vibrant image.
Yes, you can see the difference
Contrast sways image quality more than any other measurable trait. Not everyone agrees on accurate color, or gamut, or the ideal brightness. Tools can measure these elements to see if they match agreed standards, but a grassy plain that looks eerily real to one person may look false and neon to another. Perception is a factor.
But everyone agrees that a higher contrast ratio is better. The higher the ratio, the better a display can define the difference between bright and dark. That’s an essential part of reality. Open your eyes in a pitch-black room and you may find yourself terrified by the complete absence of light. Try to look at the sun, and you’ll literally injure yourself.
No screened device made by man can replicate the contrast of the real world, but the closer a display comes, the better it looks. That’s why OLED is so important. It can render the deep, murky, soul-sucking absence of light that’s a basic, primal part of the human experience.
The revolution starts small
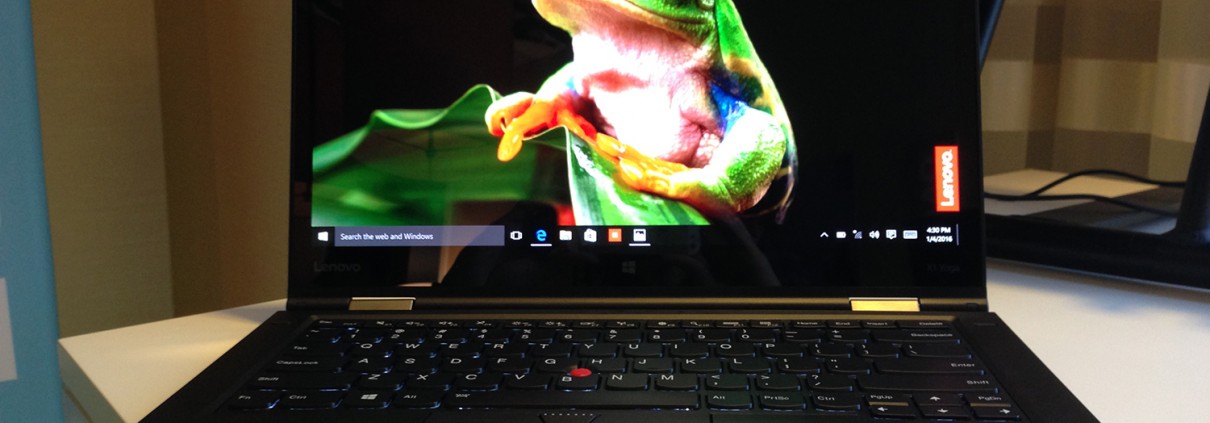
So far, four notebooks have an OLED display – the Alienware 13, the Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Yoga, the HP Spectre x360 13-inch, and the Samsung Galaxy TabPro S. All are small notebooks, with 1,440 vertical pixels. From my conversations with each company, it seems Samsung is the source of these panels, which would explain why the systems share similar Spring launch dates.
I almost feel bad for anyone who has purchased a monitor in the last few years.
They’re expensive, sadly. We only have an estimated price of the Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Yoga, which will be around $1,650 with OLED display, and that’s without any other hardware upgrades over the base model. Most people will not be able to afford a laptop with OLED screen in 2016, or even in 2017.
But the dam has broken. When one company seizes the opportunity to introduce new technologies, others must follow. We saw that with 4K displays. Toshiba was the first to introduce a laptop with Ultra HD back in April 2014. Less than two years later, every major manufacturer has a 4K panel available on at least one laptop. The tight margins of the PC business can make it hard for expensive technology to gain a foothold, but once it does, it spreads like wildfire. No one can afford to be left out.
Time to replace your monitor
I almost feel bad for anyone who has purchased a monitor in the last few years. We’ve seen some excellent sets lately, and the best have near-perfect color accuracy, but contrast has been stagnant for years. Monitors that are half a decade old, or older, can sometimes compete with today’s best.
That’s no longer true. As OLED trickles down we’ll see inexpensive monitors that blow away the image quality of last year’s best, like the Dell UP2715K and Samsung 32D970Q. Your eyes will never want to go back to the dark ages of backlit displays.

, 16
The X1 Yoga with the OLED panel uses virtually the same case as the IPS model. The wedge-shaped base unit is made from one material, which is called “Super Magnesium” by Lenovo. It is a special kind of magnesium alloy, so Lenovo can make the X1 Yoga lighter without compromising the stability. The display cover on the other hand is made of carbon. You cannot see the two materials from the outside since Lenovo wrapped the whole chassis with a matte-black coating – a typical ThinkPad. Lenovo switched to a dark gray color scheme in 2013 and 2014, but switched back to the darker color after feedback from customers. The coating of the lid is conveniently smooth and soft, while the palm rest feels a bit more rubberized. The lid is resistant to fingerprints, and simple to clean. You can see fingerprints more on the base unit and it is harder to clean.
The stability of the case is good, but you can notice the light construction compared to devices with unibody metal cases. Both the lid and the base unit can be twisted slightly, but you do not have to worry about it. It is still very sturdy for such a light and thin device. You cannot flex the palm rest, but you can the keyboard with some pressure – a result of the lift’n’lock construction, where the frame locks the keys in tablet mode. Contrary to the first test model of the Yoga X1, we did not notice any creaking sounds from our unit.